Covid Vaccination Pregnancy Pubmed
The NNV to prevent severe maternal COVID-19 was 4122058 and to avoid mechanical ventilation was 13716857. In the United States by 10 February 2021 20000 pregnant people had received a COVID-19 vaccine and enhanced pharmacovigilance of these vaccine recipients had raised no red flags 7.
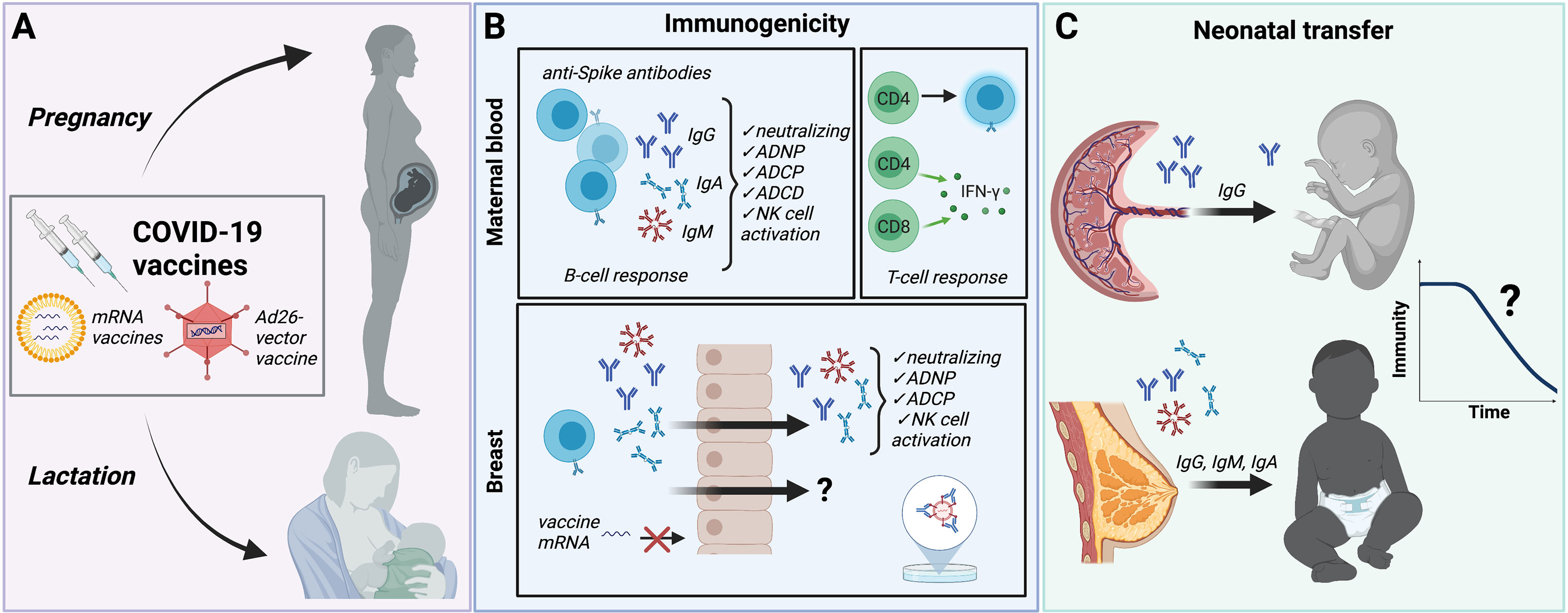
Frontiers Covid 19 Vaccination In Pregnancy And Lactation Current Research And Gaps In Understanding Cellular And Infection Microbiology
Absolute estimates of the NNV based on point estimates of the benefits versus risks of COVID-19 vaccination in pregnancy are provided in the appendix along with methodological information.

Covid vaccination pregnancy pubmed. Researchers will measure the development and durability of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 the virus that causes COVID-19 in people vaccinated during pregnancy or the first two postpartum months. When pregnant women wish to be vaccinated doctors must explain that long-term adverse reactions to COVID-19 vaccination have not been identified and that safety for fetuses and offspring has not been established. Considering benefit the NNV to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in pregnancy ranges from 11 to prevent any infection to 206 to prevent one symptomatic infection.
While pregnant and lactating women were largely not included in COVID-19 vaccine trials two studies yesterday in Science Translational Medicine look at how the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines affect the groups differently than nonpregnant women and at how the sex of the fetus may affect maternal immune response and vertical antibody transmission. COVID-19 vaccination Pregnancy breastfeeding and COVID-19 vaccines. If youre pregnant you can get a COVID-19 Pfizer vaccine Comirnaty at any stage of your pregnancy.
Vaccine hesitancy among young women is largely driven by false claims that covid-19 vaccines could harm their chances of future pregnancy13 Failing to thoroughly investigate reports of menstrual changes after vaccination is likely to fuel these fears. When pregnant people receive an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy their bodies build antibodies against COVID-19 similar to non-pregnant people. By monitoring the outcomes for these people and their babies we will soon be able to make evidence-based recommendations on whether the vaccines should be rolled out to pregnant people more widely.
A new observational study has begun to evaluate the immune responses generated by COVID-19 vaccines administered to pregnant or postpartum people. This means COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy might help protect babies against COVID-19. Pregnant women are not ineligible for COVID-19 vaccination in light of the current spread of COVID-19 infection.
Antibodies made after a pregnant person received an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine were found in umbilical cord blood. NewsRescue In a recent paper titled Be aware of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. There is no need to avoid getting pregnant after COVID-19 vaccination.
4 The potential harms to pregnant. More data are needed to determine how these antibodies similar to those produced with other vaccines. No safety concerns were identified in a study of more than 35000 pregnant people who received an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
This fact sheet in English explains why pregnant and breastfeeding women in Australia are advised to receive the COVID-19 vaccine. Evidence about the safety and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy has been growing from real-world use. 4 5 Clinical trials demonstrate that vaccination is highly effective in preventing symptomatic COVID-19 in non-pregnant patients.
The doctor should obtain consent and follow up the pregnant woman in the hospital for 30 minutes. These recommendations also apply to pregnant and recently pregnant eg up to 6 weeks postpartum individuals who completed their initial COVID-19 vaccine or vaccine series prior to pregnancy. So is COVID-19 vaccination safe during pregnancy.
Accordingly we advocate that pregnant women should be included in the phase 3 trial protocols of adenovirus-vectored vaccines and also protein-based vaccines. Pregnant and recently pregnant people can receive any COVID-19 vaccine available to them for their booster dose. Repeated a scientific warning on the potential danger of the Spike protein in vaccines and on the Covid virus.
In this study we estimated that the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine is as effective for pregnant women as previously reported for the general population during the same time period. Getting the COVID-19 vaccine can prevent serious illness hospitalization and complications. Although some live vaccinations such as measles mumps and rubella and varicella are contraindicated in pregnancy all current COVID-19 vaccines are composed of double-stranded DNA or mRNA and do not carry the live virus Table.
It does not have to be the same product as their initial vaccine or vaccine series. Spontaneous abortions did not have an increased odds of exposure to a COVID-19 vaccination in the prior 28 days compared with ongoing pregnancies adjusted odds ratio 102. Pregnant women who are at increased risk of adverse outcomes from COVID-19 would be additionally harmed if they were unable to access evidence-based chemoprophylaxis from vaccine trials.
In the meantime those who are planning pregnancies. It also protects your pēpi as there is evidence that babies can get antibodies through the placenta that help protect them from COVID. Researchers also will assess vaccine safety and evaluate the transfer of vaccine.
There is more than meets the eye published in the Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents T C Theoharides et al. If a link between vaccination and menstrual changes is confirmed this information will allow people to plan for potentially altered cycles. The data shows that mRNA COVID-19 vaccines are safe for people who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Several studies have shown that the antibodies induced by COVID-19 vaccine can cross the. Pregnancy Complications Infectious prevention control. A COVID-19 vaccine was received within 28 days prior to an index date among 80 of ongoing pregnancy periods vs 86 of spontaneous abortions.
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may reduce the risk of premature delivery of the baby if it prevents infection in the mother. The data so far suggest that it is and given the increased risks associated with COVID-19 in pregnancy many pregnant people have decided to accept the vaccine. WHOs global commitment to fair access to COVID-19 vaccines should therefore include pregnant women.
There is no evidence that COVID-19 vaccines have any effect on fertility or your chances of becoming pregnant. NICHD recently awarded five institutions one-year supplemental grants totaling 167 million to explore potential links between COVID-19 vaccination and menstrual changes. It is notable that as of April 26 2021 more than 100000 pregnant women reported having received a Covid-19 vaccination and yet only a small fraction 47 have enrolled in the v-safe pregnancy.
The vaccine protects you as youre far less likely to fall seriously ill. Researchers at Boston University Harvard Medical School Johns Hopkins University Michigan State University and Oregon Health and Science University will investigate whether such changes may be linked to the COVID-19 vaccine itself or if they are coincidental the mechanism underlying any vaccine. 29 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a health advisory recommending urgent action to increase COVID-19 vaccination among people who are pregnant trying to or might become pregnant or were pregnant recently in order to prevent serious illness death and adverse pregnancy outcomes due to the coronavirus infection.
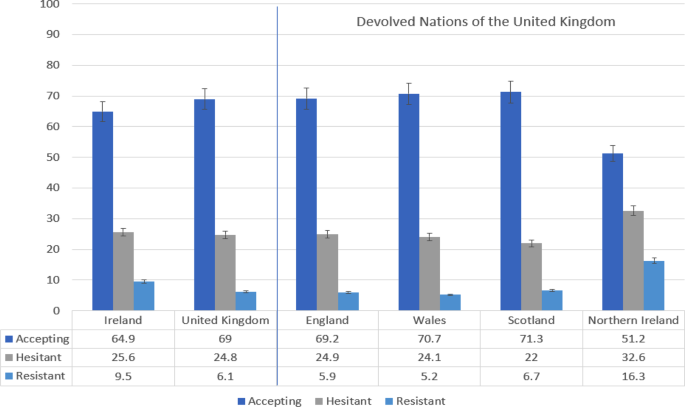
Psychological Characteristics Associated With Covid 19 Vaccine Hesitancy And Resistance In Ireland And The United Kingdom Nature Communications
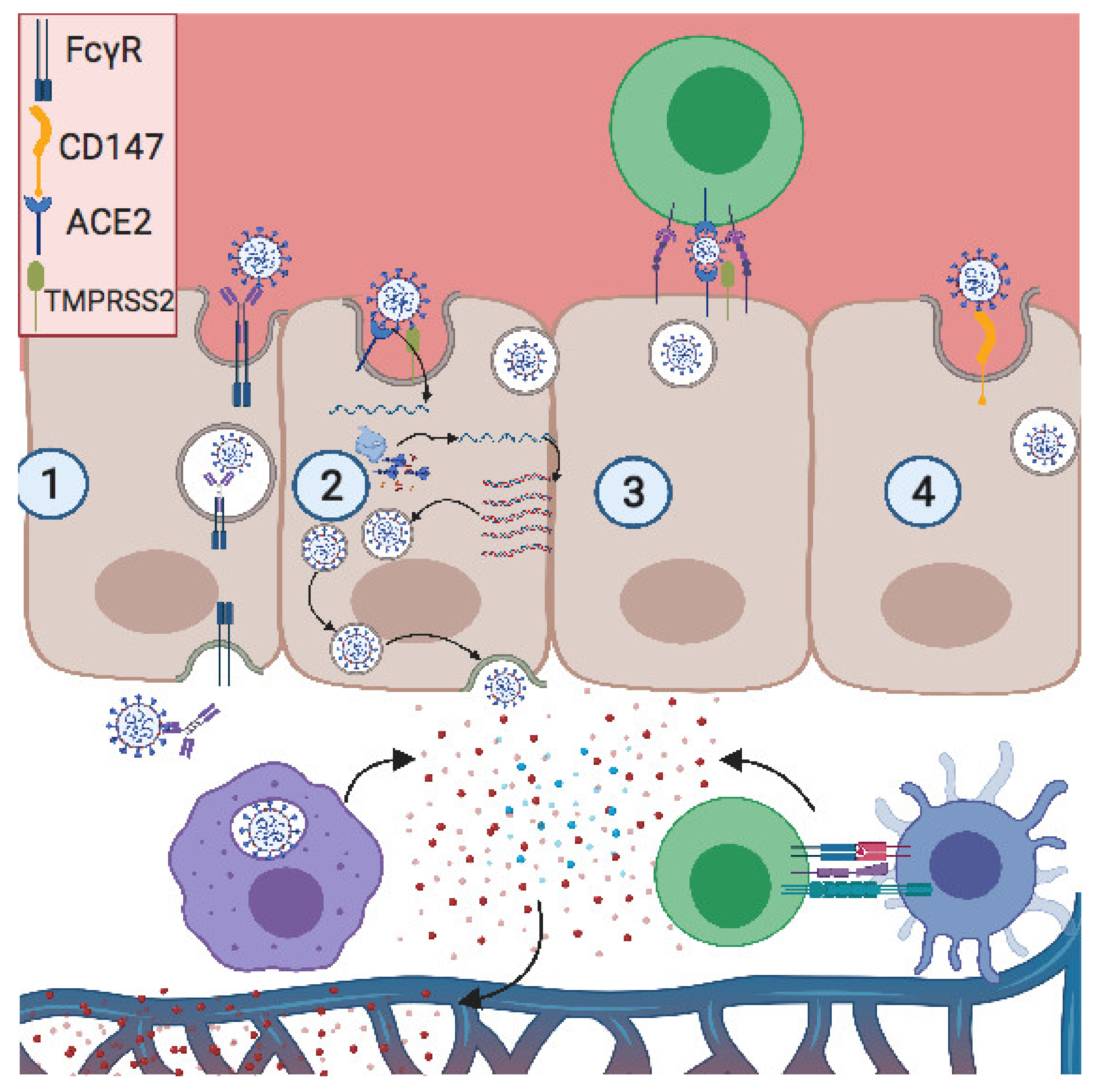
Vaccines Free Full Text Covid 19 And Pregnancy Vertical Transmission And Inflammation Impact On Newborns Html

Severe Covid 19 During Pregnancy And The Subsequent Premature Delivery Pediatrics Neonatology

Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccine Response In Pregnant And Lactating Women A Cohort Study American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology

Pregnancy And Covid 19 Physiological Reviews
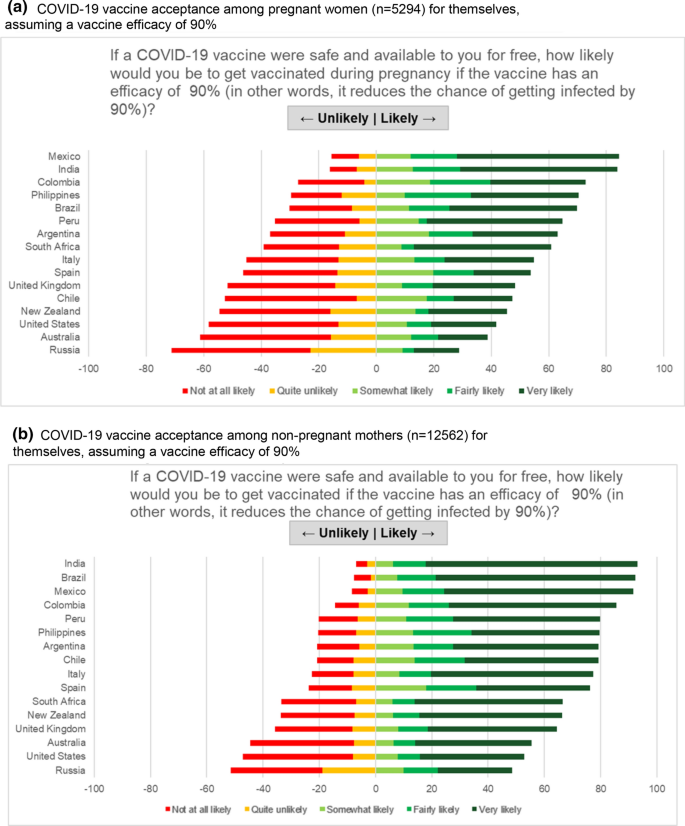
Covid 19 Vaccine Acceptance Among Pregnant Women And Mothers Of Young Children Results Of A Survey In 16 Countries Springerlink
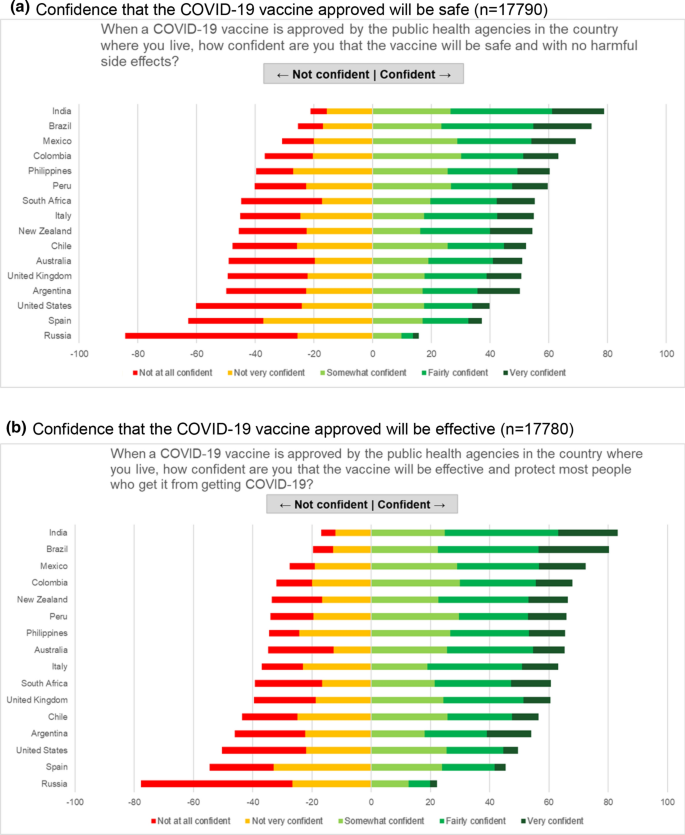
Covid 19 Vaccine Acceptance Among Pregnant Women And Mothers Of Young Children Results Of A Survey In 16 Countries Springerlink
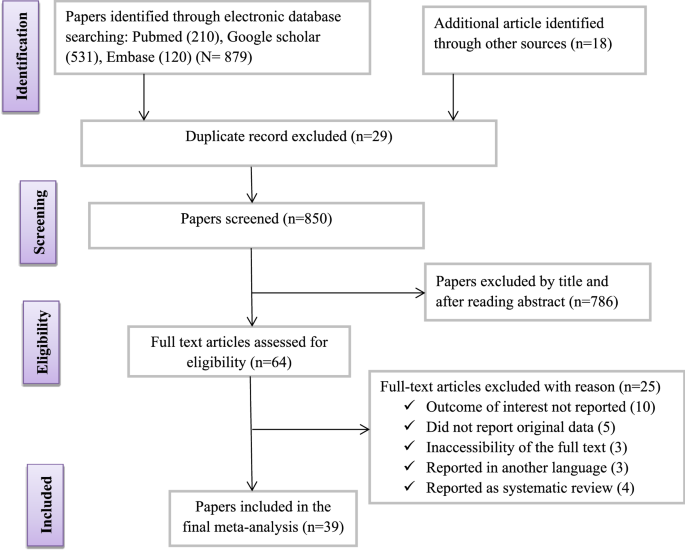
The Effect Of Coronavirus Infection Sars Cov 2 Mers Cov And Sars Cov During Pregnancy And The Possibility Of Vertical Maternal Fetal Transmission A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis European Journal Of Medical Research Full Text

Covid 19 Vaccine Hesitancy In A Representative Working Age Population In France A Survey Experiment Based On Vaccine Characteristics The Lancet Public Health

Attitudes Acceptance And Hesitancy Among The General Population Worldwide To Receive The Covid 19 Vaccines And Their Contributing Factors A Systematic Review Eclinicalmedicine
Cdc Yes People Who Are Trying To Become Pregnant Now Or Who Plan To Try In The Future May Receive The Covid 19 Vaccine When It Becomes Available To Them There Is
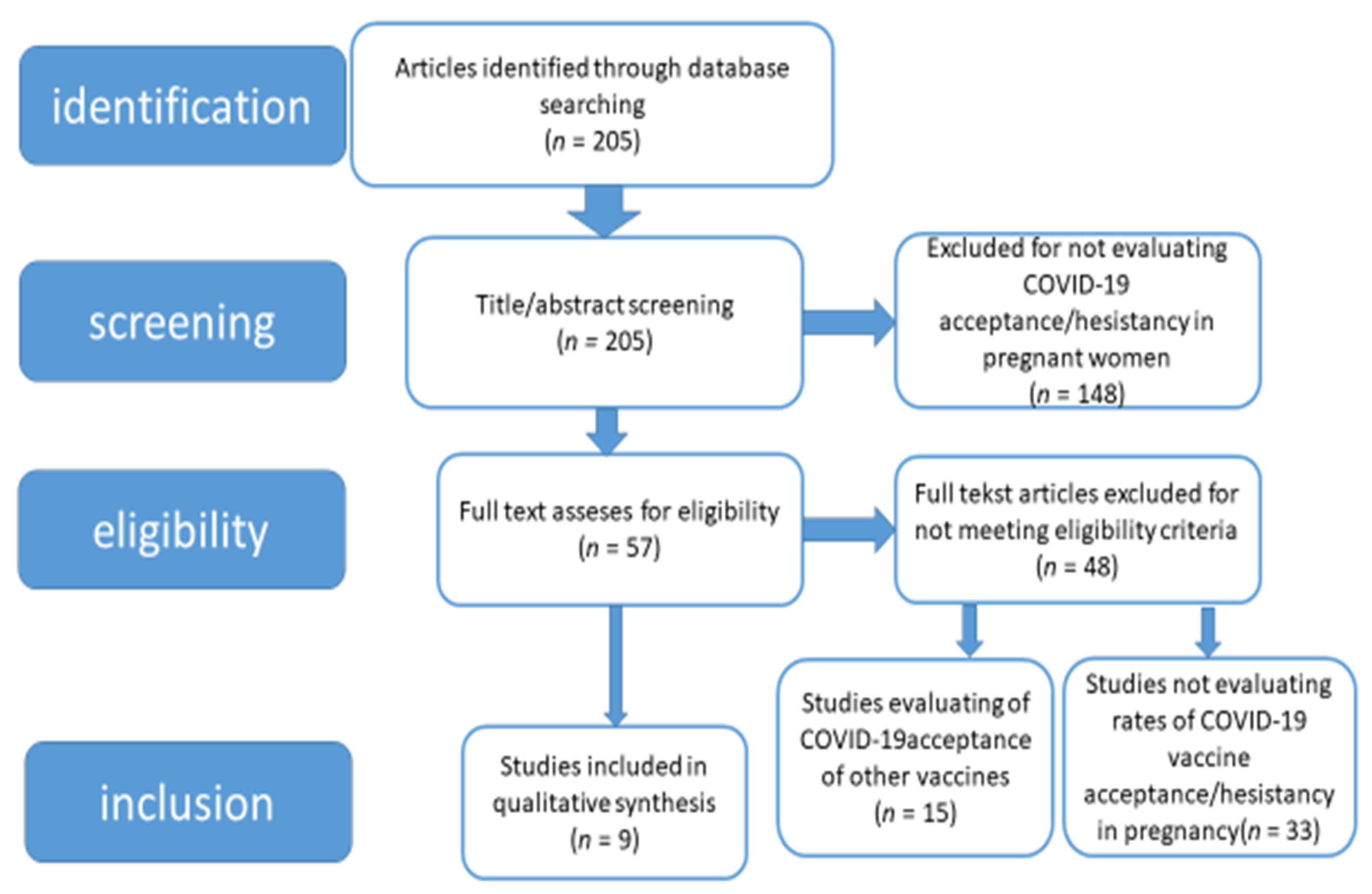
Medicina Free Full Text The Approach Of Pregnant Women To Vaccination Based On A Covid 19 Systematic Review Html

An Interactive Website Tracking Covid 19 Vaccine Development The Lancet Global Health

Covid 19 Vaccine Acceptance Among Health Care Workers In The Kingdom Of Saudi Arabia International Journal Of Infectious Diseases

Safety And Efficacy Of Single Dose Ad26 Cov2 S Vaccine Against Covid 19 Nejm
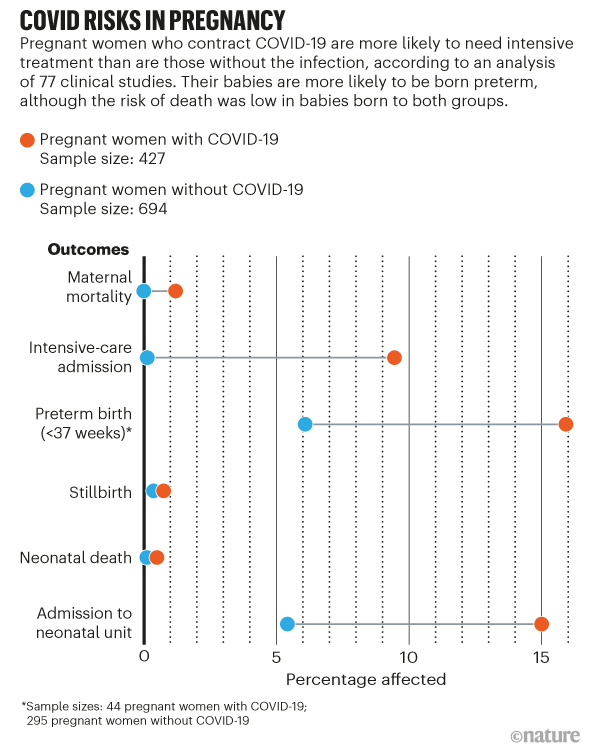
Pregnancy And Covid What The Data Say
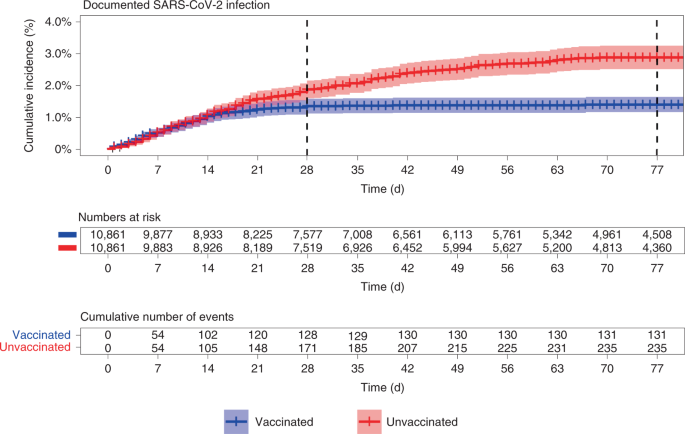
Effectiveness Of The Bnt162b2 Mrna Covid 19 Vaccine In Pregnancy Nature Medicine
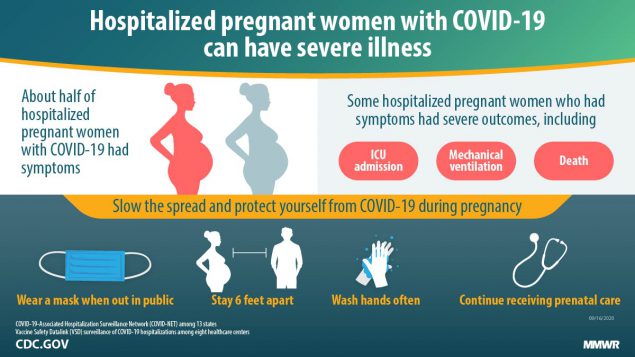
Sars Cov 2 Infection Among Hospitalized Pregnant Women Reasons For Admission And Pregnancy Characteristics Eight U S Health Care Centers March 1 May 30 2020 Mmwr

Sars Cov 2 Vaccination For Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease A British Society Of Gastroenterology Inflammatory Bowel Disease Section And Ibd Clinical Research Group Position Statement The Lancet Gastroenterology Hepatology
